Research
Ultimate performance of biomedical ablation
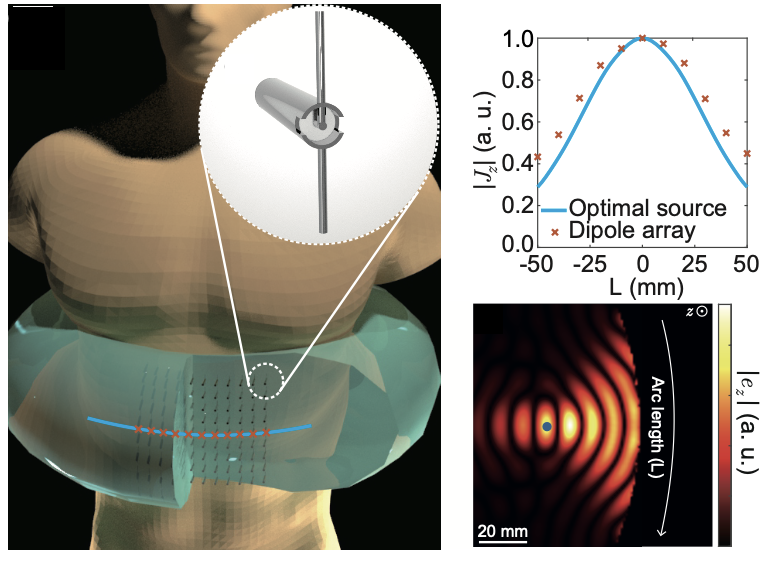 |
- Focusing the field in a confined region has been a long-sought-after goal in both microwave and optical spectrums due to its various applications, such as high-resolution microscopes, lithography, biomedicines, as well as wireless power transfer systems. Among those, microwave ablation for biomedical applications is different from the others; (i) the human tissue in which the wave travels is a lossy medium, (ii) the depth of the target can be comparable to the source size, which is limited by the body scale. These distinctive features make focusing methods for other applications not directly applicable to biomedical ablation. There are two types of ablations; the thermal one aims to raise the temperature at the target, while the non-thermal one induces a temporarily high electric field at the target to disrupt cellular membrane integrity. We study the fundamental bounds of the efficiency for each type of ablation and the sources to achieve them.
- Supporting Grants :
정보통신기획평가원 생체 내 전파 에너지 비침습 정밀 집속 기술개발(2021.06-2023.12)
- Relevant Publications :
S. Lee, Q. J, Lim, C. Ross, E. Lee, S. Han, Y. Kim, Z. Peng, and S. Kim*, ‘‘Quantum annealing for electromagnetic applications’’, under review, 2024
S. Lee, J. Lee, A. S. Y. Poon, and S. Kim*, ‘‘Ultimate performance of microwave tissue ablation’’, Physical Review Applied, accepted, 2024 [PDF]
S. Lee, S. Han, W. Song, K.-J. Lee, and S. Kim*, ‘‘Discrete source optimization for microwave hyperthermia using quantum annealing’’, IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 23 (3), Mar. 2024 [PDF]